
Chapter 16 Emergency Procedures
Table of Contents
Emergency Situations
Emergency Landings
Types of Emergency Landings
Psychological Hazards
Basic Safety Concepts
General
Attitude and Sink Rate Control
Terrain Selection
Airplane Configuration
Approach
Terrain Types
Confined Areas
Trees (Forest)
Water (Ditching) and Snow
Engine Failure After Takeoff (Single-Engine)
Emergency Descents
In-Flight Fire
Engine Fire
Electrical Fires
Cabin Fire
Flight Control Malfunction / Failure
Total Flap Failure
Asymmetric (Split) Flap
Loss of Elevator Control
Landing Gear Malfunction
Systems Malfunctions
Electrical System
Pitot-Static System
Abnormal Engine Instrument Indications
Door Opening In Flight
Inadvertent VFR Flight Into IMC
General
Recognition
Maintaining Airplane Control
Attitude Control
Turns
Climbs
Descents
Combined Maneuvers
Transition to Visual Flight

EMERGENCY DESCENTS
An emergency descent is a maneuver for descending as rapidly as possible to a lower altitude or to the ground for an emergency landing. [Figure 16-6] The need for this maneuver may result from an uncontrollable fire, a sudden loss of cabin pressurization, or any other situation demanding an immediate and rapid descent. The objective is to descend the airplane as soon and as rapidly as possible, within the structural limitations of the airplane. Simulated emergency descents should be made in a turn to check for other air traffic below and to look around for a possible emergency landing area. A radio call announcing descent intentions may be appropriate to alert other aircraft in the area. When initiating the descent, a bank of approximately 30 to 45° should be established to maintain positive load factors (“G” forces) on the airplane.
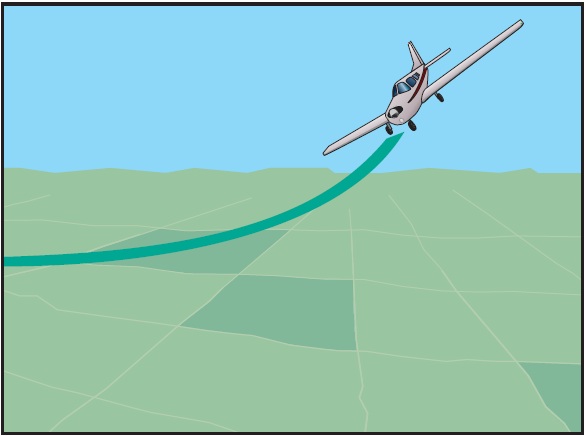
Figure 16-6. Emergency descent.
Emergency descent training should be performed as recommended by the manufacturer, including the configuration and airspeeds. Except when prohibited by the manufacturer, the power should be reduced to idle, and the propeller control (if equipped) should be placed in the low pitch (or high revolutions per minute (r.p.m.)) position. This will allow the propeller to act as an aerodynamic brake to help prevent an excessive airspeed buildup during the descent. The landing gear and flaps should be extended as recommended by the manufacturer. This will provide maximum drag so that the descent can be made as rapidly as possible, without excessive airspeed. The pilot should not allow the airplane's airspeed to pass the never-exceed speed (VNE), the maximum landing gear extended speed (VLE), or the maximum flap extended speed (VFE), as applicable. In the case of an engine fire, a high airspeed descent could blow out the fire. However, the weakening of the airplane structure is a major concern and descent at low airspeed would place less stress on the airplane. If the descent is conducted in turbulent conditions, the pilot must also comply with the design maneuvering speed (VA) limitations. The descent should be made at the maximum allowable airspeed consistent with the procedure used. This will provide increased drag and therefore the loss of altitude as quickly as possible. The recovery from an emergency descent should be initiated at a high enough altitude to ensure a safe recovery back to level flight or a precautionary landing.
16-6When the descent is established and stabilized during training and practice, the descent should be terminated. In airplanes with piston engines, prolonged practice of emergency descents should be avoided to prevent excessive cooling of the engine cylinders.
Ch 16.qxd 5/7/04 10:30 AM Page 16-7PED Publication